Non-Binary Tree(General Tree)
1. General Tree
1-1. Definition & Terms
노드가 child를 0 또는 1개 이상으로 가질 수 있는 tree를 뜻한다.
기본적인 term(root, parent, subtree..)들은 binary tree와 동일하다.
1-2 Preorder Traversal
general tree에서도 똑같이 동작한다. Root - 1st left subtree - 2nd subtree - ... - nth subtree로 방문
static <E> void preorder(GTNode<E> rt){
PrintNode(rt);
if(!rt.isLeaf()){
GTNode<E> temp = rt.leftmostChild();
while(temp != null){
preorder(temp);
temp = temp.rightSibling();
}
}
}1-3. Postorder Traversal
general tree에서도 똑같이 동작한다. 1st left subtree - 2nd subtree - ... - nth subtree - Root로 방문
1-4. Inorder Traversal
어느 타이밍에 root node를 방문할지가 확실치 않다. 그렇기 때문에 general tree를 방문하는데에는 Inorder traversal이 적절하지 않다.
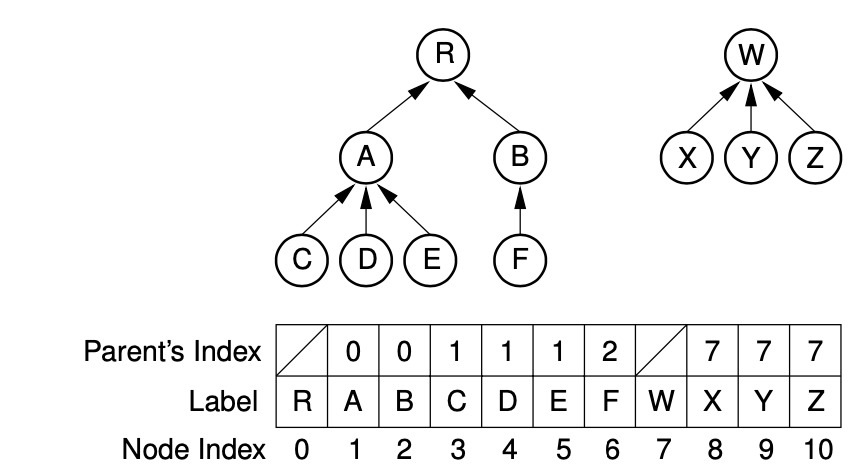
1-5. Parent Pointer Implementation
Array로 parent pointer를 implement 할 수 있다. 해당 cell이 Root node인 경우 null이다.
해당 implement를 사용해서 root node가 같은지를 확인하여 같은 트리에 소속되어 있는지를 확인할 수 있다.
/*return the root of the curr's tree*/
public Integer FIND(Integer curr){
if(array[curr] == null) return curr;
while(array[curr] != null)
curr = array[curr];
return curr;
}/* Determine if nodes in different trees */
public boolean differ(int a, int b){
Integer root1 = FIND(a);
Integer root2 = FIND(b);
return root1 != root2;
}
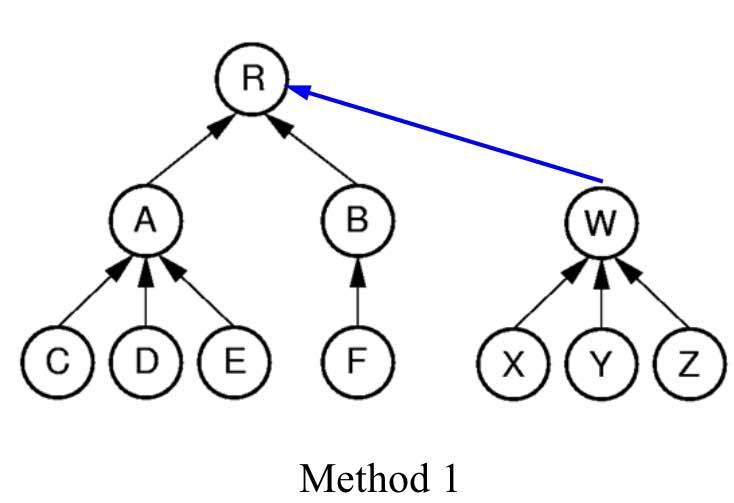
두개의 트리가 다를 때, 합쳐주는 UNION implement를 사용해줄 수 있는데,
우선 differ로 두개의 노드가 다른 트리에 속한지 확인한 후 Union을 통해 합쳐준다.
public void UNION(int a, int b){
Integer root1 = FIND(a);
Integer root2 = FIND(b);
if(root1 != root2) array[root2] = root1;
}해당 방식으로 parent node의 값을 저장하는 array[n]으로 총 n개의 node를 가지는 disjoint한 tree들을 표현한 것을 ParPtrTree라고 한다.
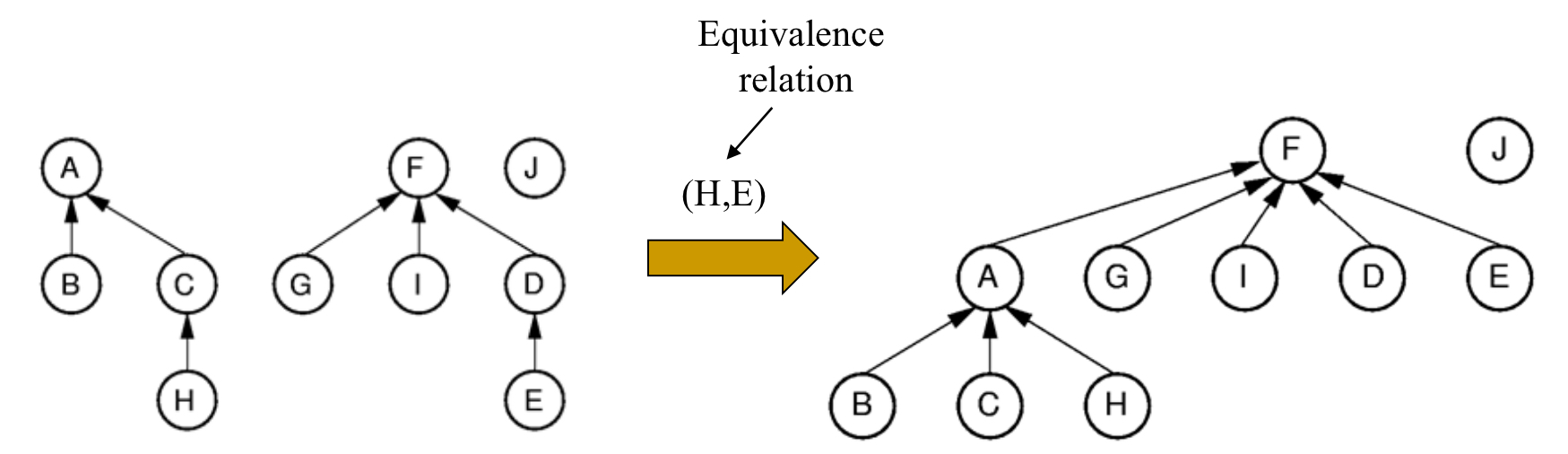
1-6. Equivalence Classes Problem
두개의 Disjoint한 set을 하나의 set으로 할당시키는 것을 equivalence classes problem이라 한다.
Union/Find algorithm으로 구현 가능하며, equivalent하다는 것은 node끼리 연결되어 있다는 것을 의미한다.
PatPtrTree에서 Union과 Find의 시간 복잡도는
Find : O(logn)
Union : O(Find(n)) = O(logn)
이 된다.
이를 위해 tree의 height를 최대한 낮게 하는 것이 좋다.
Weighted union rule : 노드가 적은 트리가 노드가 큰 트리에 합쳐지는 방식으로 합쳐진다.
Theorem : n개의 independent한 class를 가진 node가 있을 때, weighted union rule을 사용해서 union을 진행한다면 만들 수 있는 tree의 최대 높이는 logn이다.
Proof : node v를 포함하고 있는 가장 큰 깊이를 가진 최종 트리를 가정해보자. 최초의 v의 깊이는 0이다. v의 깊이는 v가 포함된 subtree A가 더 많은 node를 가진 subtree B와 합쳐질 때만 증가한다. 그러므로 v의 최대 깊이는 v의 depth가 증가할 수 있는 횟수와 같다. 따라서 logn.
1-7. Path Compression
어떻게 하면 tree의 깊이를 더 줄일 수 있을까? => Find를 할 때 거쳐간 node마다 자신의 root를 부모로 가지도록 한다.
/* FIND for path compression */
public Integer FIND(Integer curr){
if(array[curr] == null) return curr;
array[curr] = FIND(array[curr]);
return array[curr];
}2. General Tree Implementation
parent(), leftmostChild(), rightSibling()을 얼마나 잘 구현하는가가 평가의 기준이 된다.
2-1. List of Children
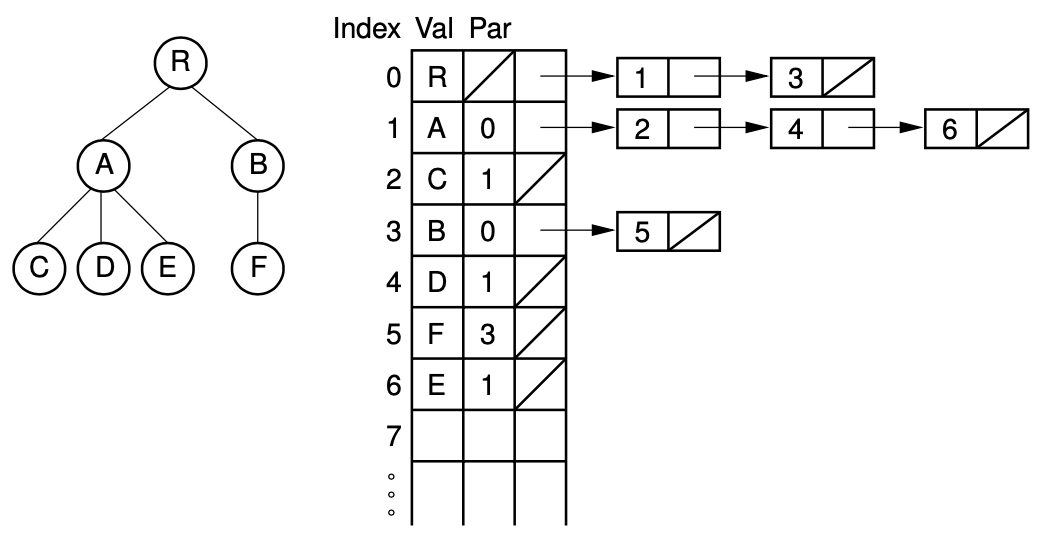
parent pointer와 children을 linked list로 저장
장점 :
(1) parent()가 효율적이다.
(2) leftmostChild()가 효율적이다.
(3) 만약 두 트리 모두 같은 array에 속한다면 합치기 쉽다.(같은 index 정보를 사용)
단점 :
(1) rightSibling()이 비효율적이다.
(2) array based implementation이기 때문에 사전에 최대 node 수를 미리 할당해둬야 한다.
2-2. The Left-Child / Right-Sibling Implementation
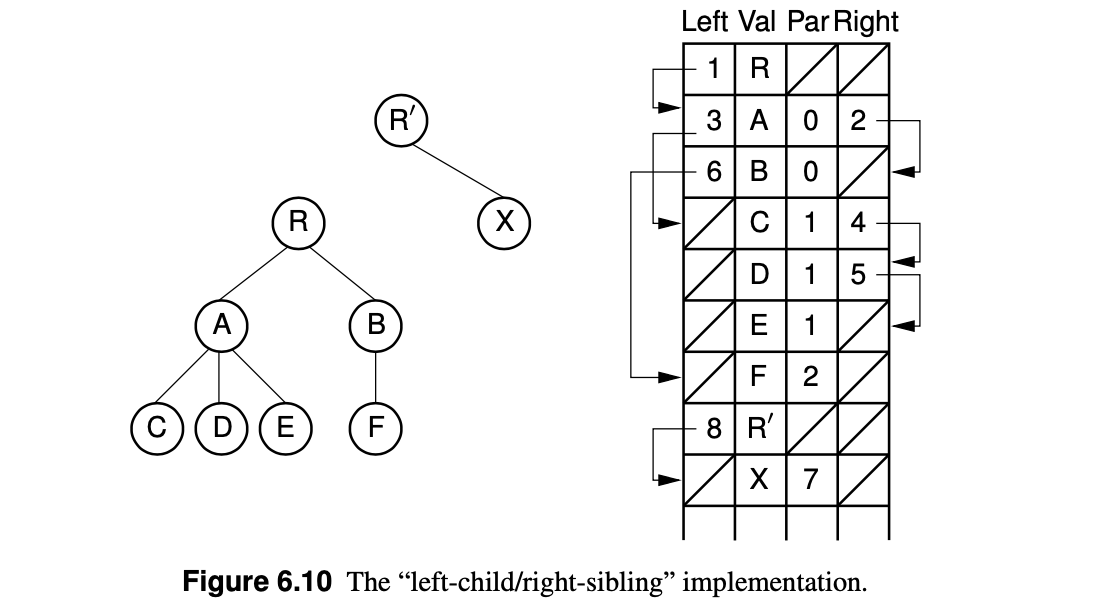
Right sibling 정보를 함께 저장해둔다.
장점 :
(1) parent(), leftmostChild(), rightSibling()이 모두 효율적이다.
(2) 같은 array에 있을 때 두 subtree를 합치기 쉽다.
(3) pointer를 위한 공간을 낭비하지 않아도 된다.(list of children과의 차이)
단점 :
(1) array based implementation이 문제.(미리 최대 node 수를 알아야 함)
2-3. Dynamic Node Implementation
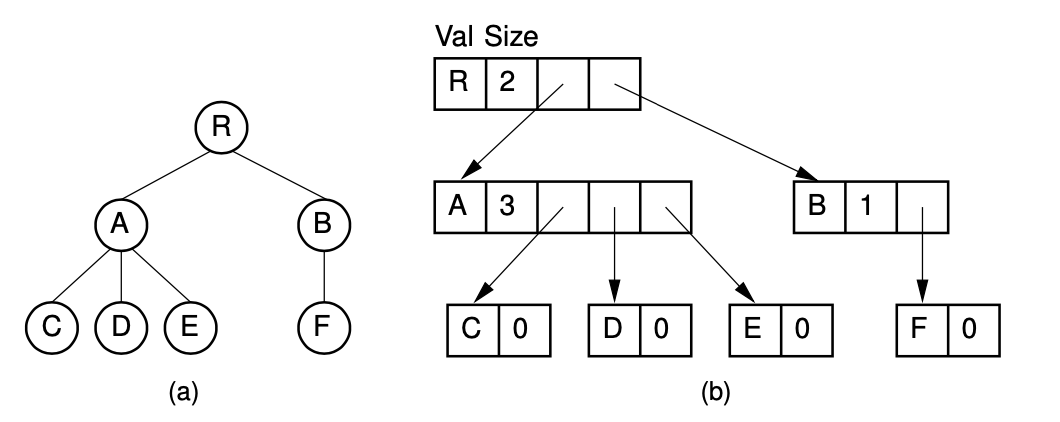
각각의 노드를 서로 Pointer로 연결시키는 방식으로 구현한다.
장점 :
(1) parent()가 효율적
(2) leftmostChild가 효율적
(3) 두개의 subtree를 합치기가 쉽다.
(4) 최대 node의 수를 미리 알지 않아도 된다.
단점 :
(1) rightSibling()이 비효율적이다.
(2) childnode가 얼마나 될지 미리 할당해 놓아야한다.(child의 갯수에 따라 각 노드의 array 크기가 달라지기 때문에)
2-4. Dynamic Node Implementation(ver 2)
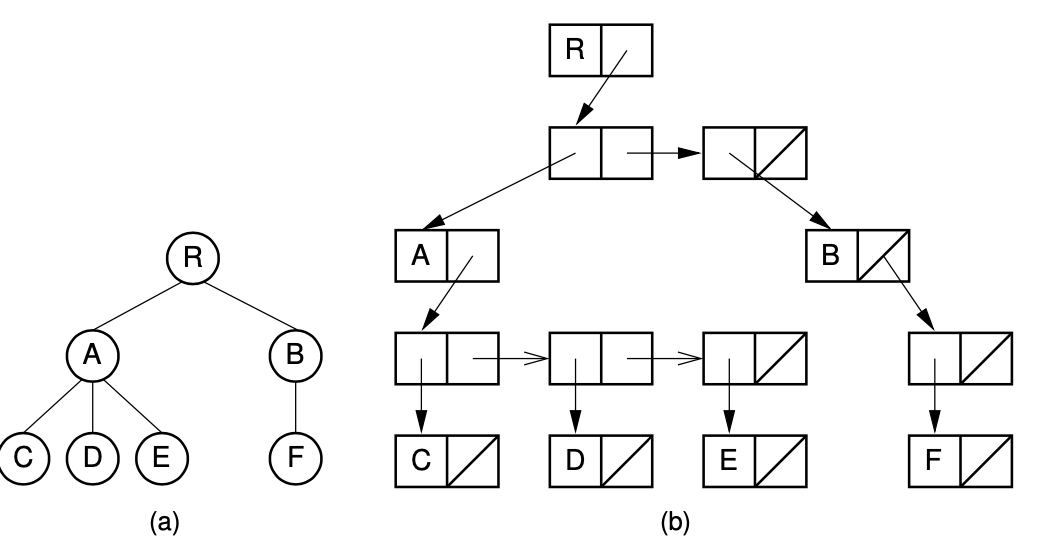
각각의 노드는 array size가 2이다.
장점 :
(1) 위의 구현에 비해 훨씬 flexible하다.
단점:
(1) 위의 구현에 비해 space를 더 많이 필요로 한다.(pointer)
2-5. Dynamic "Left-Child/Right-Sibling" Implementation
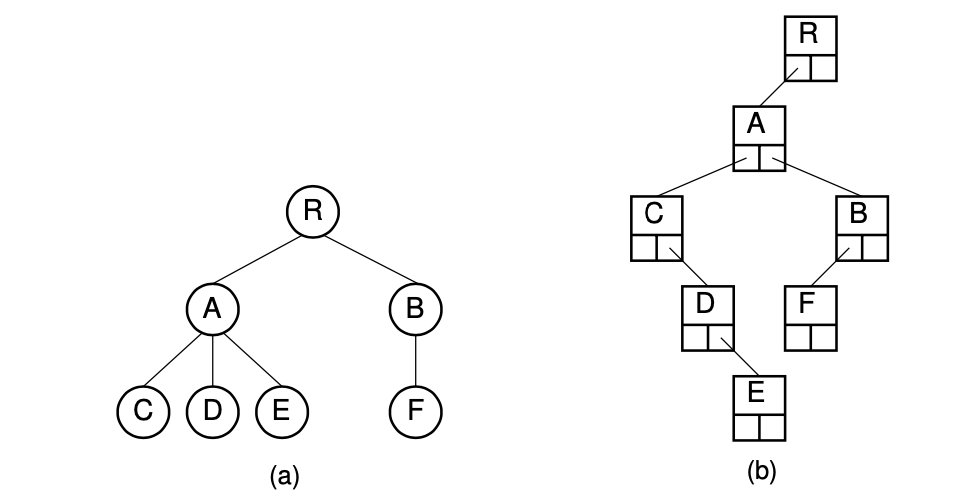
장점 :
(1) linked가 가진 장점을 모두 가짐
(2) 위의 (ver2)보다 space efficient하다.
2-6. Sequential Implementation
space만 신경쓰고 implement하고 싶을 때 사용한다.(parent(), leftmostChild(), rightSibling())을 고려하고 싶지 않을 때)
preorder traversal 순서에 맞춰 value를 정렬한다.
pointer는 따로 저장되지 않고, 오로지 sequential access만 허용된다.
해당 표현만 보고 tree를 reconstruct할 수 있어야 한다.
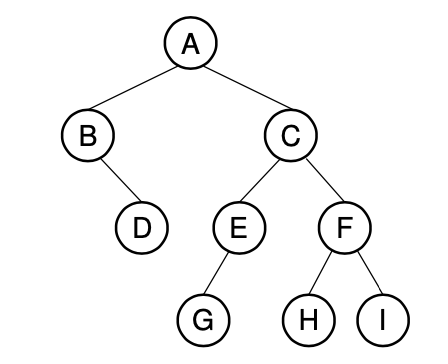
(binary tree)
idea1) null 링크를 표현하기 위해 '/' 기호를 사용한다.(예를 들어 B는 null link 1개, D의 경우 2개)
AB/D//CEG///FH//I//
null pointer 때문에 space overhead가 1/2가 된다. (because of full binary tree corolloy)
idea2) internal node를 표현하기 위한 1bit짜리 정보를 추가한다.
A'B'/DC'E'G/F'HI
full binary tree에서는 '/' symbol이 사용되지 않는다.
full binary tree의 경우 space overhead가 1/32 (4bytes 중 1bit만을 사용)
(General tree)
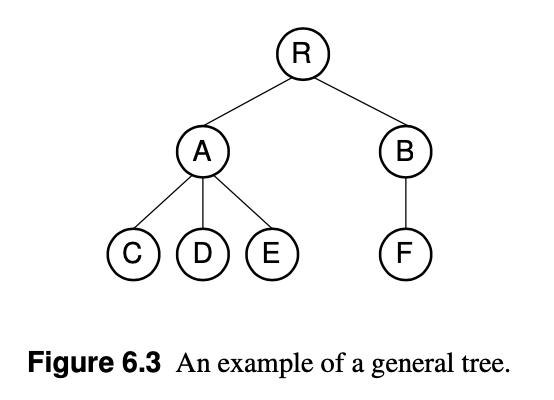
end of each subtree를 ')'로 표현한다.
RAC)D)E))BF)))
binary tree의 경우 해당 방식으로 표현이 불가능하다! -> F node의 경우 해당 표현 방식으로 left node인지 right node인지 알 수 없기 때문이다.